Installation of QDK
Before we can start using QDK we have to install it. It is distributed as a platform-independent QPKGpackage and can be installed using the normal web interface. When installed and enabled QDK is ready to beused.
At installation a directory structure is created at the default QPKG location, which depends on whether it isinstalled on a RAID volume or a single drive. The exact location is available in the QDK_PATH variable in thesystem-wide configuration file, \/etc\/config\/qdk.conf, but it is usually \/share\/MD0_DATA\/.qpkg\/QDK on aRAID system and \/share\/HDA_DATA\/.qpkg\/QDK on a single drive system.
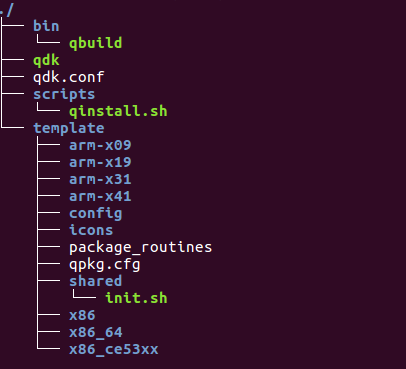
qdk is the init script used to enable and disable QDK. This script is run automatically when QDK is enabledor disabled in the web interface. It creates and removes a symbolic link to the qbuild application in \/usr\/bin.
qbuild is the build script.
qinstall.sh is the part of the installation script that includes the generic installation functions common to allQPKG packages. This file is never edited by the user. All user defined actions are added to a separate file,package_routines.
The template directory include files for a new build environment that can be created using qbuild. By defaultit includes common subdirectories where the content should be placed and templates for the package specificinstallation functions, package_routines, the QPKG configuration file, qpkg.cfg, and an init-script. The init-script, init.sh, is renamed to the same name as the package when the new build environment is created.
There are also four hidden files, .qpkg_icon.gif, .qpkg_icon_80.gif, .qpkg_icon_gray.gif, and .uninstall.sh.The three first files are the default icons used for QDK in the web interface and the last file is the script runto perform the required actions to clean up after QDK when it is removed using the web interface. This file iscreated automatically for all QDK based packages at installation time.